
[Expert Answer] Draw the molecular orbital diagram for F2 and find out the bond order Brainly.in
Energy-Level Diagrams. Because electrons in the σ 1 s orbital interact simultaneously with both nuclei, they have a lower energy than electrons that interact with only one nucleus. This means that the σ 1 s molecular orbital has a lower energy than either of the hydrogen 1s atomic orbitals. Conversely, electrons in the \( \sigma _{1s}^{\star } \) orbital interact with only one hydrogen.

29 F2+ Molecular Orbital Diagram Wiring Database 2020
A dihydrogen molecule ( H2 H 2) forms from two hydrogen atoms. When the atomic orbitals of the two atoms combine, the electrons occupy the molecular orbital of lowest energy, the σ σ 1s bonding orbital. A dihydrogen molecule, H 2, readily forms, because the energy of a H2 H 2 molecule is lower than that of two H atoms.
MO Diagrams for First Row Diatomic Molecules Chemistry LibreTexts
Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram for F2 (2+) 28,328 views 9.5 Molecular Orbital Theory | General Chemistry Chad's Prep When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma (2p) bonding molecular.

Molecular Orbitals
The bond lengths are inverse to the bond order, so the order is F2+ < F2 .There is 1 unpaired electron in F2+, 0 unpaired electrons in F2. Q12.14 Which of the following molecules have the shortest bond: F 2. Draw the molecular orbital diagram of \(Ne_2\) and \(Ne_2\). From that, describe the bonding scheme of those two molecules based on.

Molecular Orbital Diagram Of F2 My XXX Hot Girl
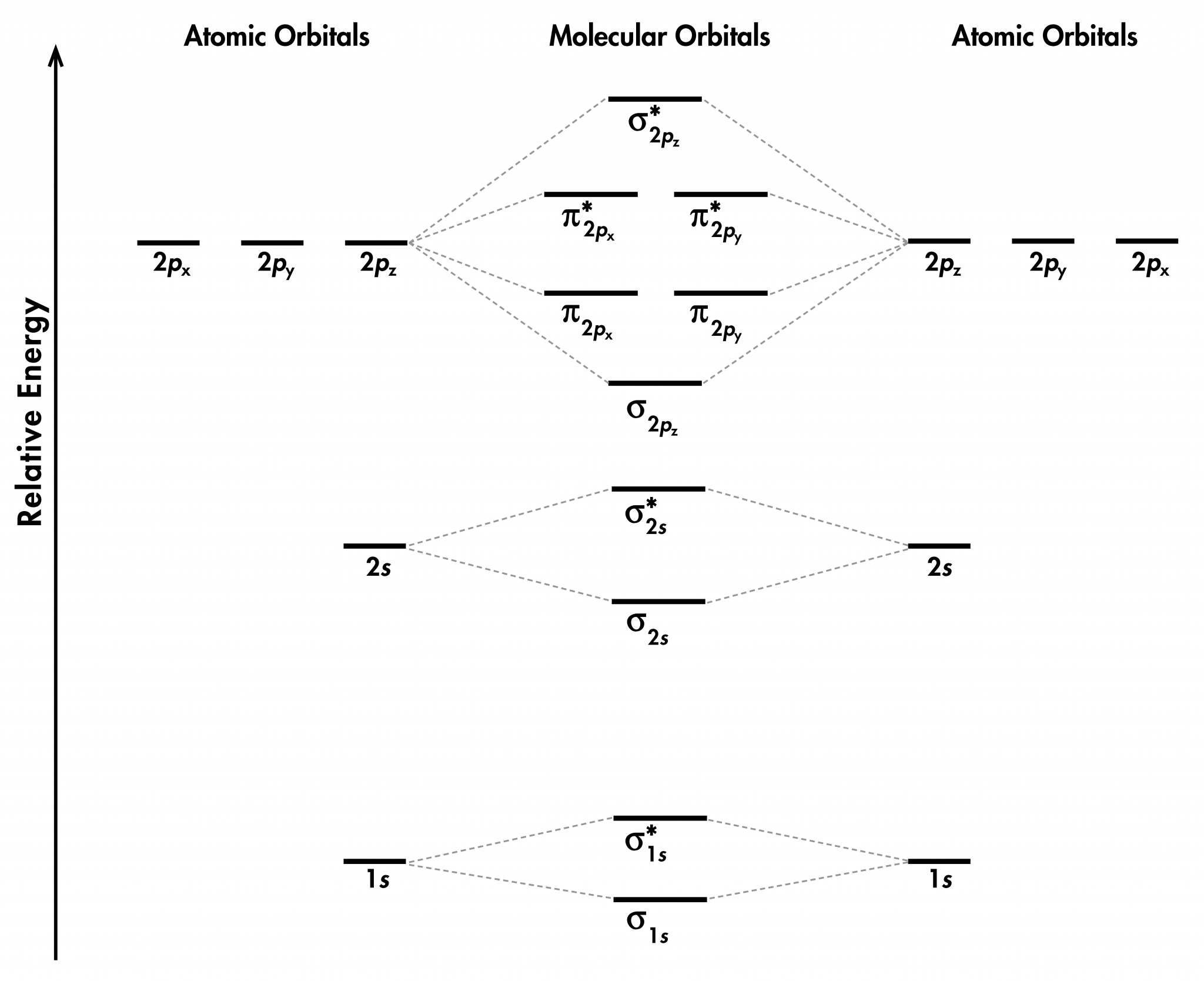
Figure 8.4.4 8.4. 4: Combining wave functions of two p atomic orbitals along the internuclear axis creates two molecular orbitals, σp and σ∗p σ p ∗. The side-by-side overlap of two p orbitals gives rise to a pi (π π) bonding molecular orbital and a \ ( π^*\) antibonding molecular orbital, as shown in Figure 8.4.5 8.4. 5.

F2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Polarity, and MO Diagram Techiescientist
Step 1. Start by calculating the number of valence electrons in each atom of F2 and see how many more electrons each fluorine atom needs to form an octet. The atomic number of fluorine is 9; therefore, it possesses 9 electrons in its neutral atomic form. There are 2 electrons in its K shell and 7 electrons in its L shell.
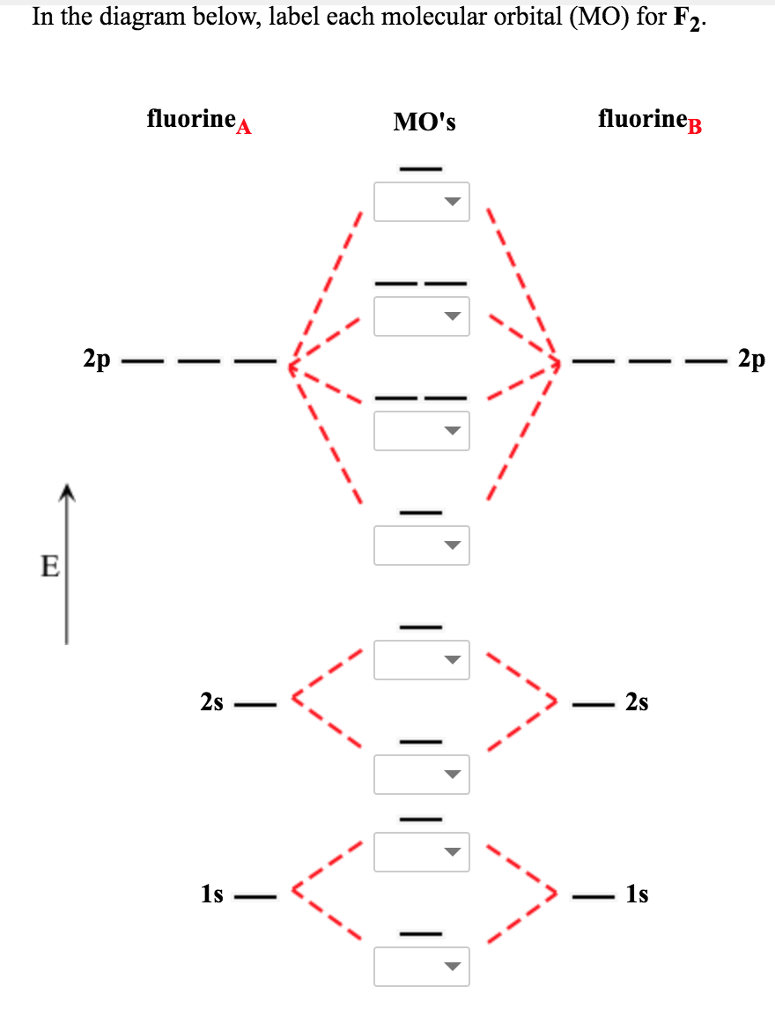
Chemistry Molecular orbital diagrams
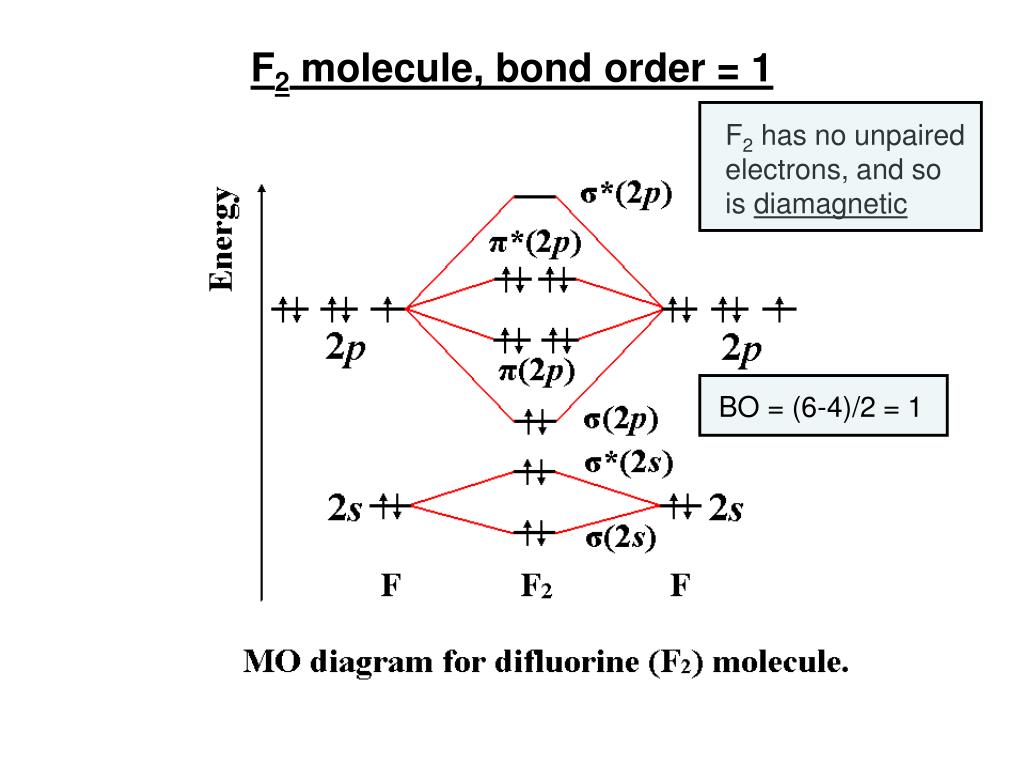
The F2 molecule is known for its strong bond, which is predicted by the presence of strong bonding orbitals in the molecular orbital diagram. The presence of sigma and pi bonding orbitals indicates a stable molecular structure, making the F2 molecule highly reactive and able to form strong bonds with other atoms or molecules.

How to draw Molecular Orbital Diagram for F2 Molecular Orbital Theory Diagram Chemistry
Physical & Theoretical Chemistry Supplemental Modules (Physical and Theoretical Chemistry) Chemical Bonding Molecular Orbital Theory MO bonding in F2 and O2

Draw the molecular orbital diagram for F2 and find out the bond order Brainly.in
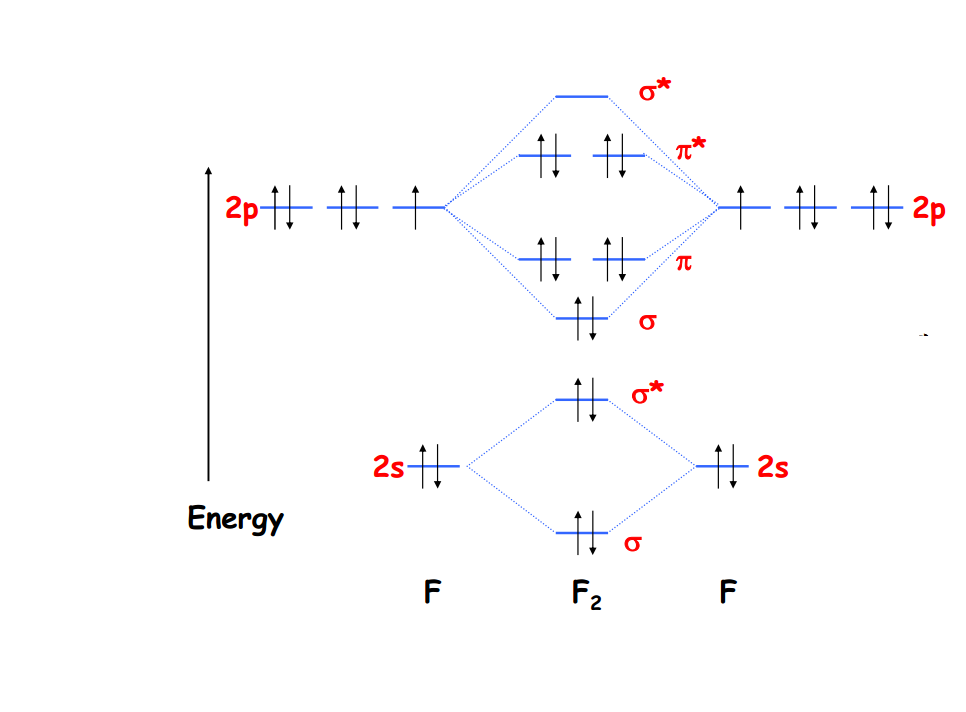
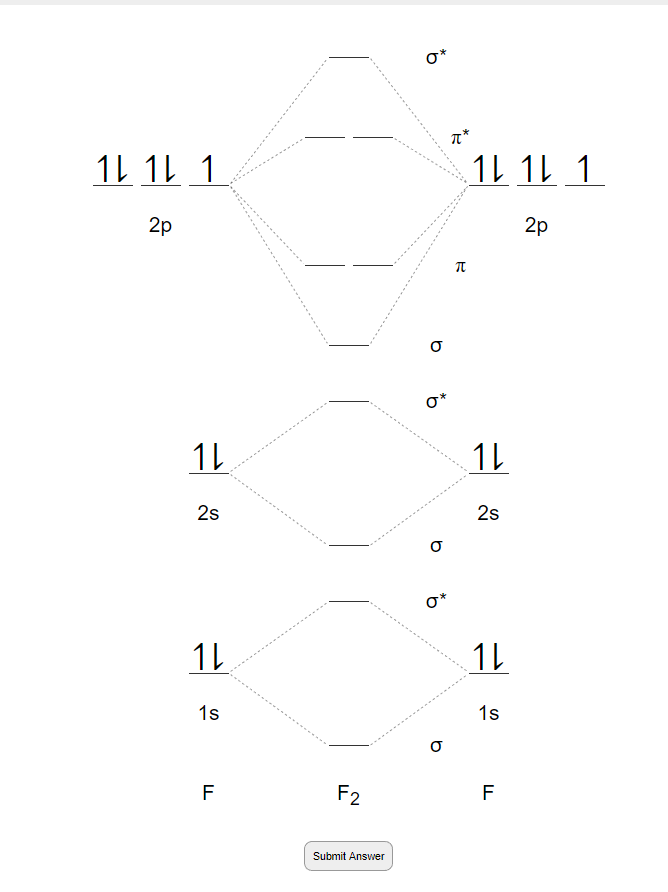
1. Write down the electronic configuration of F2 atoms F 2 consists of two fluorine (F) atoms. The electronic configuration of each F-atom is 1s2 2s2 2px2 2py2 2pz1. Usually, only the valence electrons are displayed in the MO diagram of a molecule, therefore, it is important to note that each F-atom contains 7 valence electrons.
F2 2 Molecular Orbital Diagram Wiring Diagram
Molecular orbital diagram F2 bond order When two fluorine atoms get involved to form the F2 molecule, the fluorine molecule atomic orbitals are also involved in the formation of F2 molecule. As the F atom has 1s 2 , 2s 2 , 2p 5 electronic configuration and having total 18 electrons but four electrons from 1s orbital will not get involved in bonding.
Day 6 Molecular Orbitals; Lewis Structures Chemistry 109, Fall 2020
Bond lengths for each basis set, along with electrostatic potential, HOMO and LUMO molecular orbitals for F2. Because F2 is a diatomic molecule, the bond angle is assumed to be 180 degrees for , due to the molecule being linear. A valence energy level diagram from F2 is shown in Figure 1. The button F2 PM3 will appear in the box below.
43 molecular orbital diagram f2
The molecular orbital diagram of F2 showcases the molecular bonding and antibonding orbitals formed when two fluorine atoms combine. These molecular orbitals are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals from each fluorine atom, creating a new set of orbitals that extend over the entire molecule.
Molecular Orbital Diagram For F2 General Wiring Diagram
Orbital Mixing Orbitals of similar but unequal energies can interact if they have the same symmetry The 2s and 2p orbitals form MOs with the same symmetry (σ z g and σu). sp mixing causes the σ and σ g u MOs to be pushed apart in energy: The σ and The size of the effect depends on the 2s-2p energy difference. small Z = eff

Molecular Orbital Diagram Of F2 Molecule The highest energy occupied molecular orbital in the
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of.

molecule orbital F2
Draw molecular orbital diagrams for the following molecules/ions: F2+, F2, and F2-. Identify which of the three is the most stable and determine the bond order for each.. Orientations of D Orbitals (0) Intro to Crystal Field Theory (0) Crystal Field Theory:. 12. Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory MO Theory: Bond Order. 3 PRACTICE.
Molecular Orbital Diagram For F2 Wiring Site Resource
0:00 / 4:36 Molecular Orbital Diagram for F2 and F2+ Brandon C 7 subscribers Subscribed 5.6K views 3 years ago Here is a video that discusses over the Molecular Orbital Diagram for.